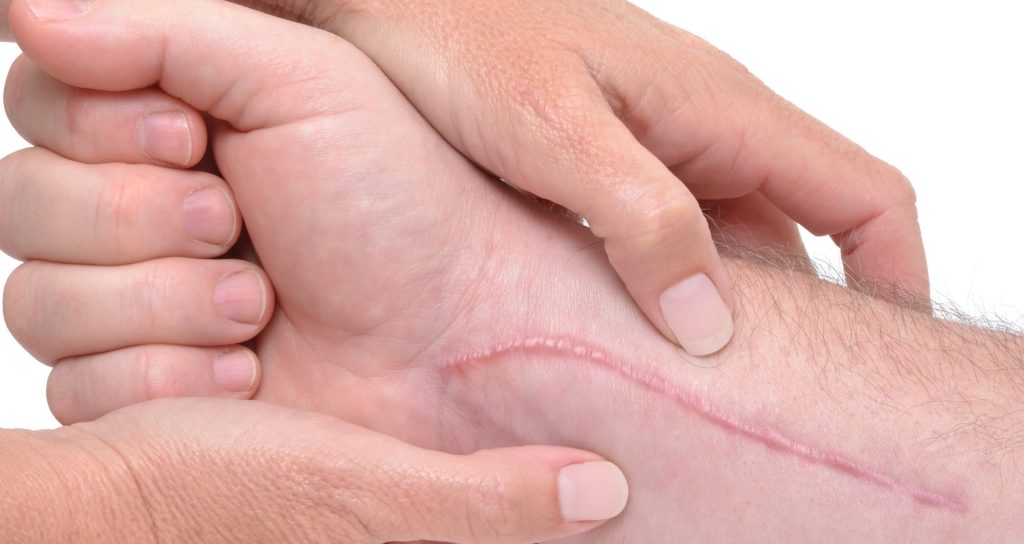
Our skin is the first defence line for our body against the external threats and it forms the 15% of body weight as the largest organ after the skeleton system. (5) Wound or wound damage is the damage to the anatomic and functional integrity of skin and subcutaneous tissues which are epidermis, dermis and panniculus due to any trauma. (1, 5) As a result of any deterioration on the skin, new tissue begins to form at the site of the damaged tissue as a result of cellular and biochemical events that start regularly and sequentially, and this is defined as wound healing. (2) Although this process looks simple, it is a series of complex events consisting of multiple stages and elements. In this article, we will look into wound types, wound shapes and reasons. (3,4)
What Are Wound Types?
Knowledge Base
Detailed information about wounds and wound types due to damaged tissue integrity...
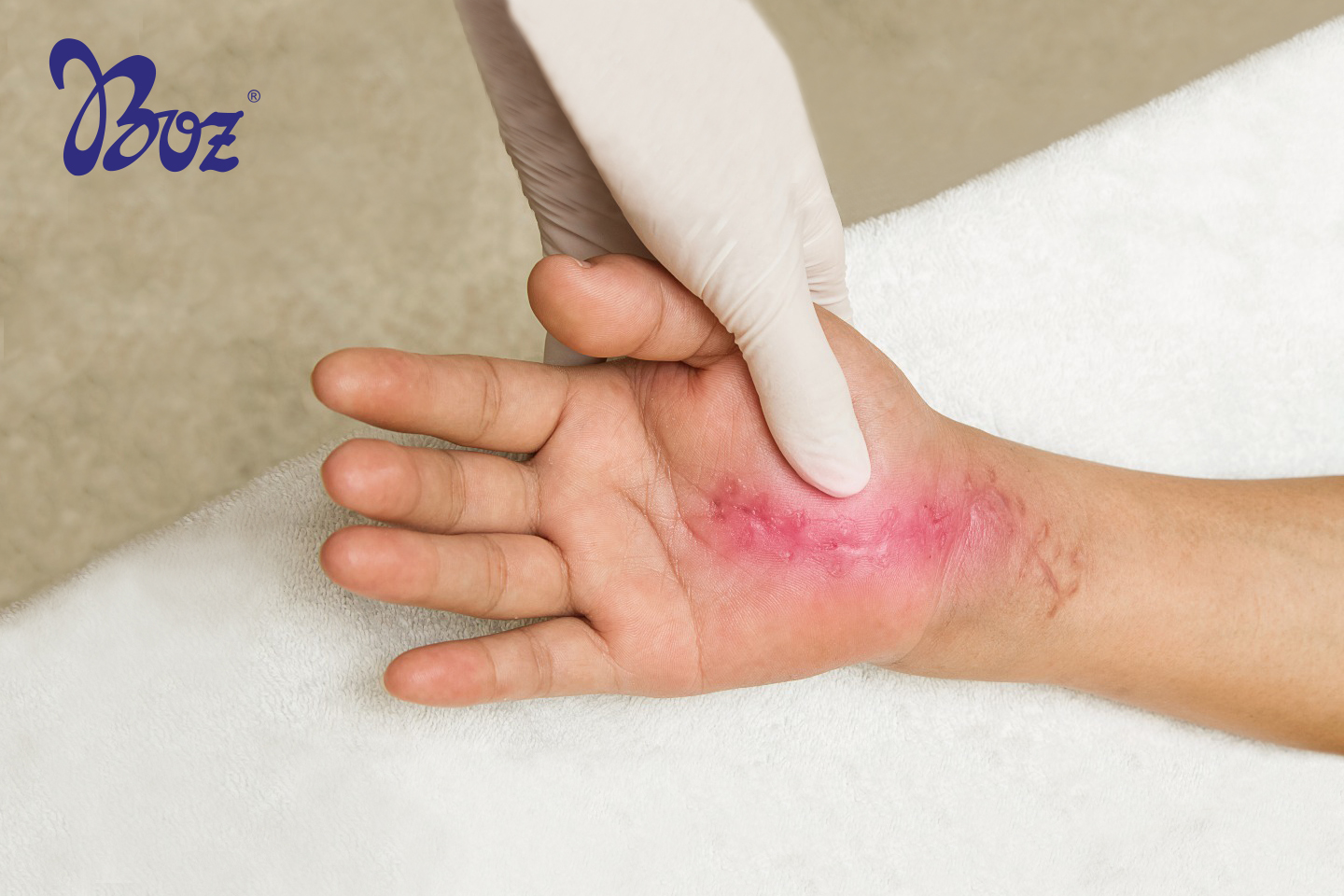
What Are Wound Types?
Wound is any damage to tissue integrity and the physiologic recovery and repair with tissue changes in the healing process following the damage. Chronic wounds are wounds that don’t heal easy and leave marks on the body.
Wounds are divided into three. The first one is erosion wounds which are superficial wounds that don’t penetrate to dermis and leave a mark. The second one is vertical wounds called fissures. The third one is ulcer which is chronic and deeper than erosion wound. These wounds penetrate to dermis, leave a mark and the treatment is hard. (5) Also, the wounds can be divided into two groups as acute and chronic wounds.
What Are Acute Wounds?
Acute wounds are wounds that start and end and fade away fast. These have temporary impact, heal faster, the number of elements to prevent healing are low and the healing is continuous. Post-op wounds or operation wounds can be given as an example to acute wounds. (5,6)
What Are The Reasons for Acute Wounds?
The name acute wound means “instantly developing” wounds. Therefore, instant “acute” wounds occur on damaged tissue after trauma. The reasons for acute wounds can be listed as contusion due to crushing of the tissue, abrasion due to shearing, laceration due to tearing, chemical or physical burns, bites made by animals or humans or surgical incisions called incisions and penetrating due to conditions such as stinging, puncture, gun injury, insect bites.
Acute Wound Recovery Period
The acute wound recovery is fast and regular when the necessary treatment is applied. There are few reasons to prevent wound healing and scar tissue formation is regular. As a result, the healing is continuous and the tissue recovers in around 4-5 weeks and go back to its former state.
What Are Chronic Wounds?
Chronic wounds are formed systematically and the healing takes a lot of time. In some cases, these wounds might not heal. The impact is continuous which means there are numerous factors such as venous, nervous or cell-based that elongate or prevent healing. Feet wounds in diabetes and cancer-related ulcers can be given as chronic wound examples. (5,6)
What Are The Reasons for Chronic Wounds?
The general factors for chronic wounds are smoking, irregular and uncontrolled nutrition and as a result of obesity, problems seen in advanced age, vitamin deficiency or trace element deficiency, malignant tumours, chemotherapy or radiotherapy methods used in cancer treatment, drugs that weaken the immune system (Warfarin, Heparin etc.) and diabetes mellitus.
Chronic Wounds In Diabetes
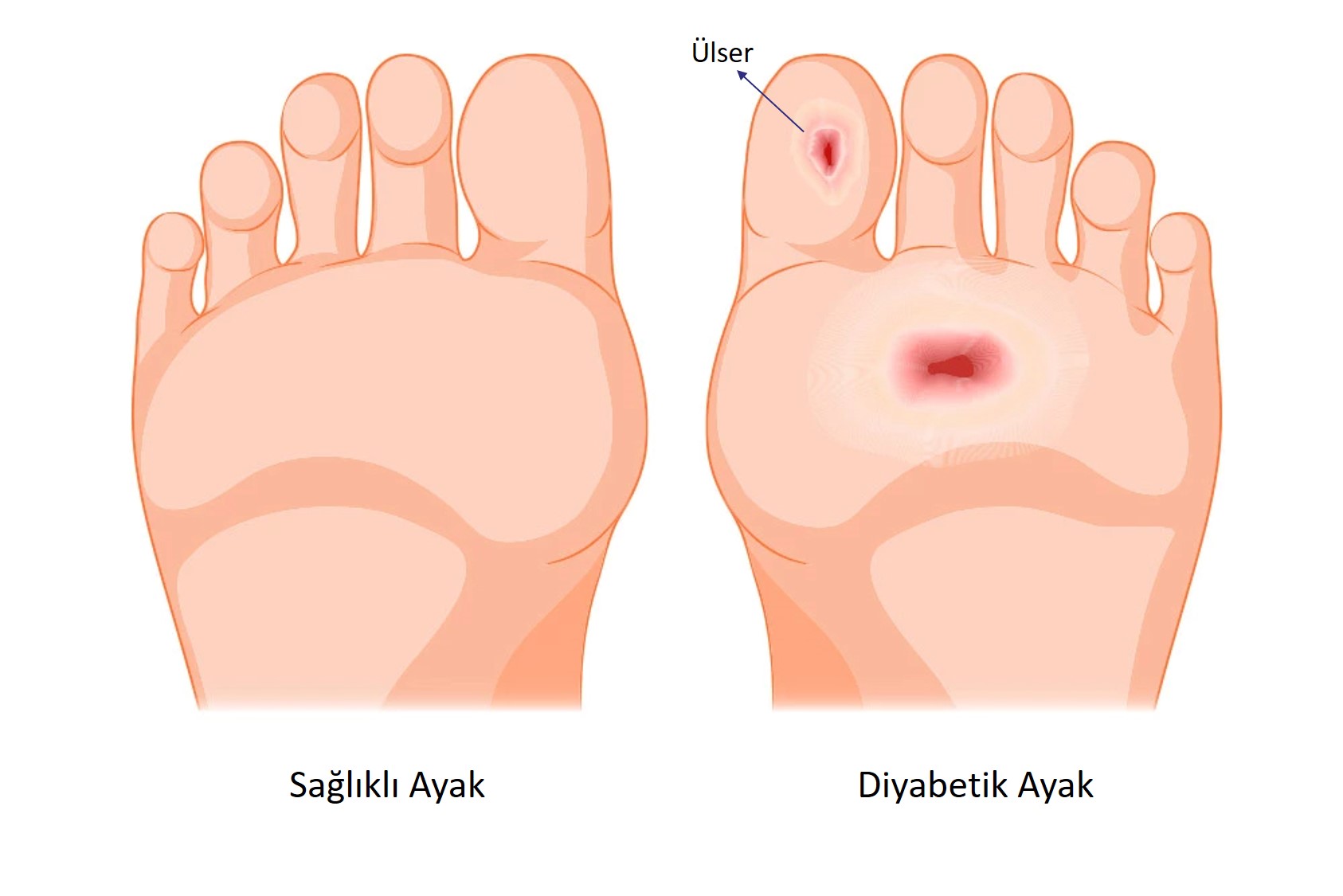
The repetitive wounds that don’t heal over time are called chronic wounds and the general factors are given above. Diabetes must be highlighted and it is one of the main diseases that cause chronic wounds. Diabetes which is a chronic diseases damaged nerves and vein tissues over time, cause blood circulation problems and lead to wounds on various parts of the body and especially on feet. When the problem progresses, it can lead to vascular occlusion and even loss of feet or legs. (8)
Varicose Vein
These wounds are often see on ankles and front part of the leg and these are formed due to malfunction of venous valve problems. The blood leaks back and accumulates in vascular access. Therefore, the pressure increases and the veins swell. (7, 8)
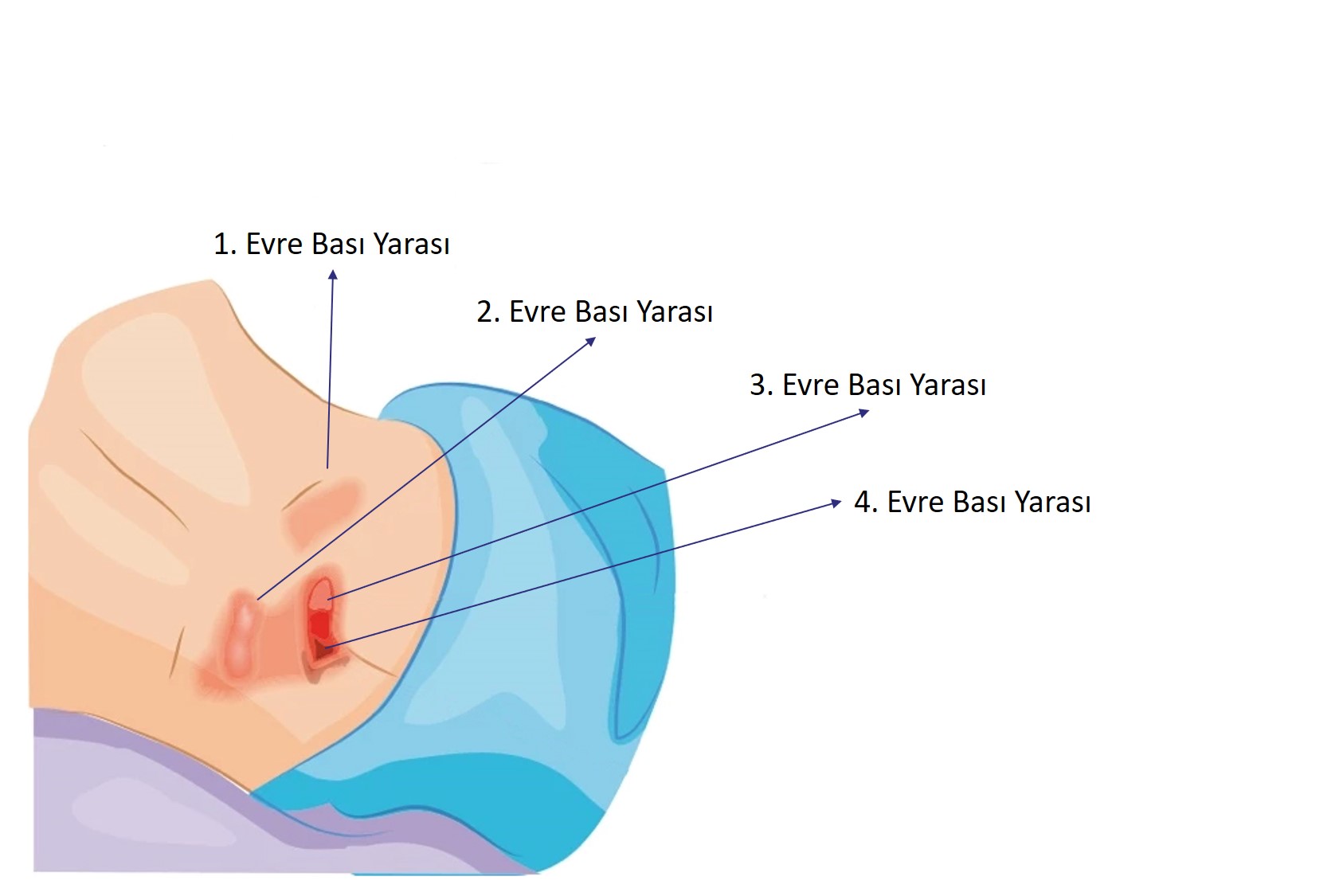
Compression Ulcers / Decubitus
This wound is often seen on bedbound or wheelchair bound patients and it is due to pressure on the same part of the body. The shape, stage and depth of the chronic compression wounds can be different.
What Are The Differences Between Open and Close Wounds?

What Is An Open Wound?
We can divide open wounds into two sub-groups. These are: These are clean cuts by sharp objects such as knife, razor or glass which are called incisions. Another open wound type is the irregular, tear-like wounds caused by blunt trauma, also known as lacerations.
- The integrity of the skin or subcutaneous tissue is damaged due to trauma.
- These are due to contusion, penetrant, laceration or incision. (see also: paragraph 4)
- The wound is not bandaged and it continuously contacts with air.
- The wound might be infected with the necessary treatment and wound dressing aren’t applied. As a result, the recovery can take longer and the wound can become deeper. (1)
Close Wounds
These wounds are blood accumulation between the tissues and tissue gaps due to trauma.
- The tissue integrity is preserved.
- These wounds can have different forms such as crush, sprain, or joint or intramuscular hematoma. (1)
What Are Wound Types for Shape?
Contusion
These are wound due to crushing the tissue by a heavy load, stone, bar or an impact from a traffic accident. The bleeding risk is low but these wounds can be life threatening due to internal organ damage. (5,9)
Incision Wounds
These are simple wounds created by glass, knife or sharp objects. The wound can be superficial or deep depending on the depth of the incision and the depth of the wound can be seen easily. Depending on the depth, these wounds can be life threatening. (5,9)
Abrasion Wounds
These wounds are the damage on the epidermis and bleeding on capillary vessels due to abrasion. There might be pain since the nerve ends are damaged. (5,9)
Penetration Wounds
These are the wounds due to penetration by a bullet, needle, sharp object or wire. Since these wounds are deep, large vessels such as arteries and internal organs might be punctured. These wounds can be life threatening or cause tetanus risk depending on the depth of the wound and the sharp object. (5,9)
Fragmented Wound
These wounds are caused by partial or complete rupture of the skin or subcutaneous tissue. Since there will be extensive bleeding, the individual might die because of blood loss. (5,9)
Bibliography
(1) Prof. Dr. Varlı M. Yara iyileşme süreci ve etkileyen faktörler. Yaşlı Bakım ve Teknikerleri Yara Bakım Eğitimi. 2019
(2) Werner S, Grose R. Regulation of wound healing by growth factors and cytokines. Physiological reviews. 2003;83(3):835-70.
(3) Hormozi M, Assaei R, Boroujeni MB. The effect of aloe vera on the expression of wound healing factors (TGFβ1 and bFGF) in mouse embryonic fibroblast cell: In vitro study. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy. 2017;88:610-6.
(4) Fizyoaktif – Medical Trainer. “Yara İyileşme Fizyolojisi” Son güncelleme 26 Ağustos, 2021. http://fizyoaktif.com.tr/?p=965.
(5) Prof. Dr. ARAS, Sevgi “Yara Nedir? Tipleri, Evrelendirme” AÜTF – Geriatri Bilim Dalı (erişim 26.08.2021)
(6) Prof. Dr. KARGI, Eksal “Kronik Yara Nedir?” Türk Plastik Rekonstrüktif ve Estetik Cerrahi Derneği (erişim 27.08.2021)
(7) Op. Dr. KARACA, Yaşar “Varis nedir? Belirti ve tedavi yöntemleri nelerdir?” Medical Park (erişim tarihi 27.08.2021)
(8) Kolan British Hospital “Kronik Yara Bakımı (Bası Yaraları, Venöz Ülserler, Diyabetik Ayak)” Son güncelleme 27 Ağustos, 2021. https://kolanbritish.com/tibbi-birimler/plastik-estetik-ve-rekonstruktif-cerrahi/kronik-yara-bakimi-basi-yaralari-venoz-ulserler-diyabetik-ayak/
(9) Sağlığım “Yara Nedir?” T.C. Sağlık Bakanlığı https://sagligim.gov.tr/yaralanmalarda-ilk-yardim/yara-nedir.html (erişim 27.08.2020)